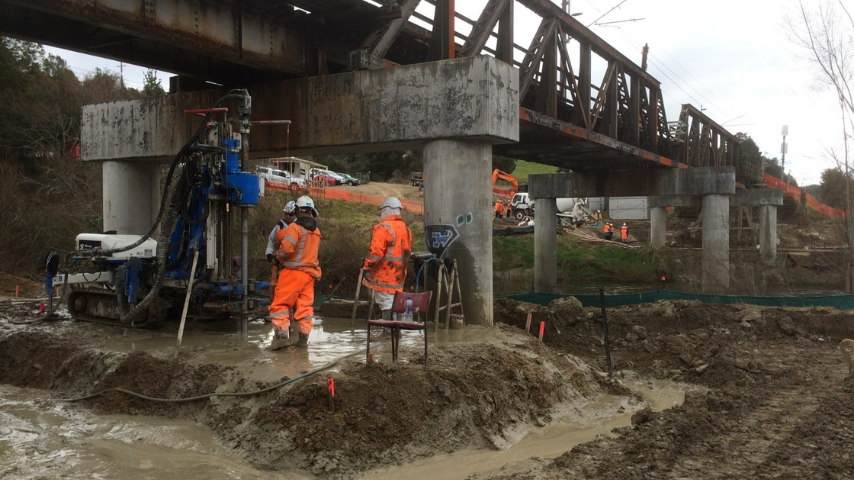
Grouting in Construction: Meaning, Types, Methods & Real-Life Examples
In the world of civil engineering and infrastructure development, grouting in construction plays a silent yet vital role. Whether it’s stabilizing foundations, sealing cracks, or anchoring equipment, grouting ensures that structures remain strong, safe, and long-lasting.
This comprehensive guide explores everything you need to know about grouting—including its meaning, types, methods, materials, equipment, and real-life applications—especially in the context of grouting in construction in India.
What is Grouting in Construction?
Grouting in construction refers to the process of injecting a fluid-like material (called grout) into voids, cracks, joints, or between structural elements to:
● Fill gaps
● Reinforce weakened zones
● Prevent water leakage
● Improve the load-bearing capacity of soil or concrete
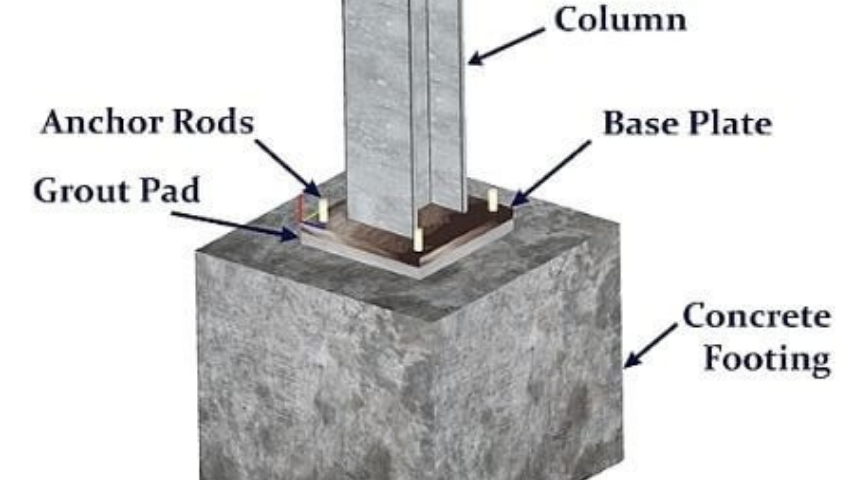
Grouting Meaning in Civil Engineering
In civil engineering, grouting is a specialized technique used in structural repairs, soil improvement, waterproofing, and anchoring applications. The process involves selecting the right grouting material and applying a suitable grouting method in construction based on the site condition and project requirements.
Purpose of Grouting in Construction
Grouting serves multiple essential functions, including
Sealing leaks in underground structures like tunnels and basements
Stabilizing soil beneath foundations or slabs
Strengthening damaged concrete or masonry
Fixing bolts, machinery, or rebars to concrete bases
Preventing ground settlement
Types of Grouting in Construction
Different types of grouting are used based on the application, environment, and structural need. Here’s a breakdown of the types of grouting in construction:
1. Cement Grouting
● Uses cement and water or sand-cement mix
● Common in dam repairs, masonry joints, and foundations
● Cost-effective and versatile
● Example: Grouting cement is used to fill cracks in RCC slabs

2. Chemical Grouting
● Uses chemical resins like polyurethane, epoxy, or acrylic
● Ideal for waterproofing or sealing fine cracks
● Expands upon injection to fill micro voids
3. Epoxy Grouting
● Made from epoxy resin and hardener
● Used for machinery baseplates and anchoring systems
● High strength and chemical resistance

4. Bituminous Grouting
● Asphalt-based
● Used in road construction and waterproofing expansion joints

5. Soil Grouting
● Also called permeation grouting
● Improves the strength and stiffness of loose or sandy soils
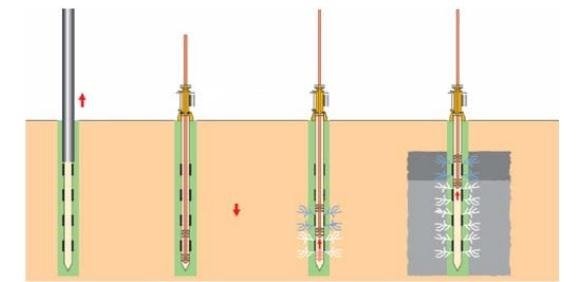
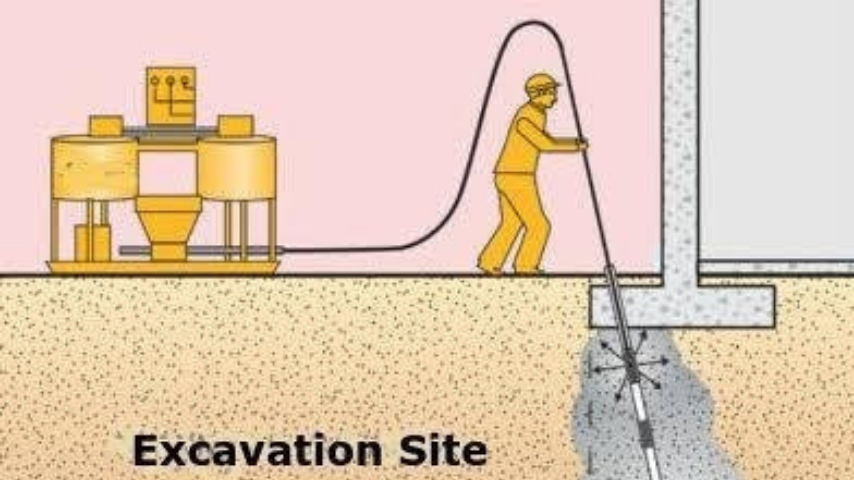
Methods of Grouting in Construction
Various grouting methods are used in construction, each selected based on the type of structure, soil conditions, and purpose—such as strengthening foundations, sealing leaks, or filling voids.

| Grouting Method | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Pressure Grouting (Injection Grouting) | Grout is injected under pressure through drilled holes. Common in structural repairs and soil stabilization. |
| 2. Permeation Grouting | Injects grout into porous soils without disturbing the ground. Used in foundations, tunnels, and pipelines. |
| 3. Compaction Grouting | Thick grout is injected to compact and displace weak soil. |
| 4. Jet Grouting | High-pressure jets create a grout-soil mixture. Effective in deep foundations or below existing buildings. |
How Foundation Grouting Saves Your Home from Cracks
Cracks in floors, walls, or the foundation can be early signs of serious structural issues. In India, where soil settlement, moisture changes, or aging buildings are common, foundation grouting is a proven method to restore stability—without major reconstruction.
What is Foundation Grouting?
Foundation grouting is a process where cement-based grout is injected under pressure into the soil or cracks beneath your home’s foundation. This fills voids, lifts settled areas, and strengthens the base.
Common Causes of Foundation Cracks:
● Uneven settlement of soil
● Water seepage below the foundation
● Poor compaction during construction
● Tree roots or underground utilities shifting soil
How Grouting Helps:
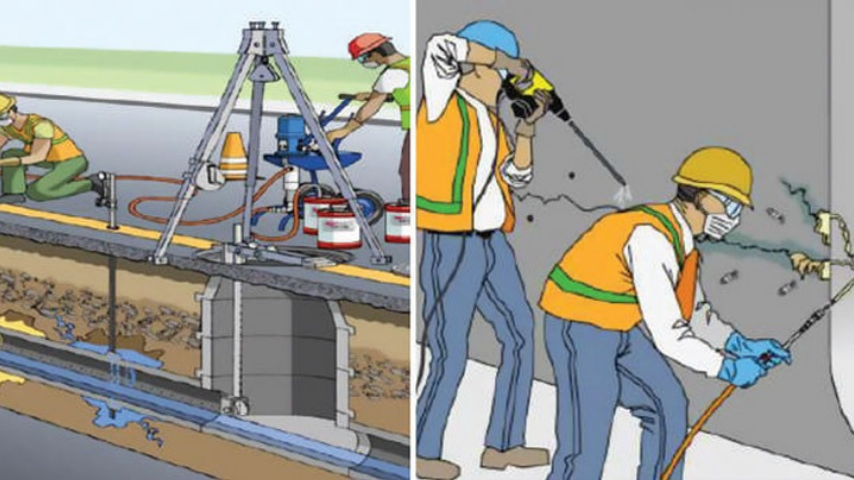
● Fills hidden voids beneath foundation slabs
● Re-levels sunken floors or plinths
● Prevents further settlement and cracking
● Restores load-bearing capacity of soil
● Saves time and money compared to total rebuilding
Real-Life Scenario (India):
In older Chennai bungalows and apartments built on clayey soil, residents often notice diagonal cracks near doors or windows. Engineers inject a non-shrink cement grout using portable grouting machines in construction to stabilize the area.
Result: Cracks stop expanding, walls become stable, and the property regains its structural integrity—without digging up the foundation.
Grouting Material and Their Properties
The success of grouting work in construction depends heavily on choosing the right grouting material:
Grouting material |
Application |
Cementitious Grout |
Concrete repair, dam joints, masonry gaps |
Epoxy Grout |
Anchoring machinery, base plates |
Polyurethane Grout |
Sealing water leaks in tunnels/basements |
Acrylic Resin Grout |
Soil injection, water cut-off |
Fly Ash or Bentonite |
Used as additives to reduce cost or improve flow |
Grouting Equipment in Construction
Modern grouting equipment in construction ensures fast, efficient, and high-quality application. Common tools include
● Grouting machine in construction (manual or automatic pumps)
● Injection packers and hoses
● Mixing drums and agitators
● Nozzles for tile or wall grouting
● Jet grouting rigs (for deep foundation soil work)

Grouting in Construction in India: Real-World Examples
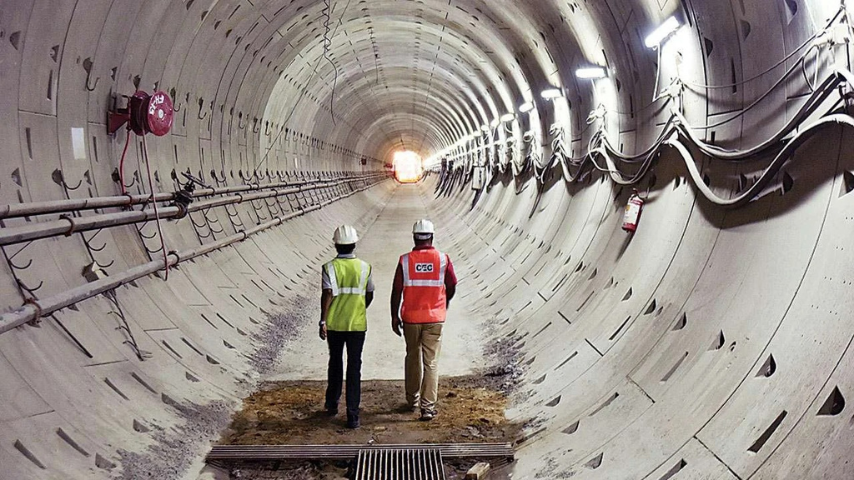
1.Delhi Metro Tunnel – Groundwater Seepage Sealed with Chemical Grouting
Location: Underground Metro Line, New Delhi
Problem: During the construction of underground metro tunnels, engineers encountered groundwater leakage through the segmental joints and cracks in the concrete lining. Left untreated, this water ingress could lead to corrosion of reinforcement, tunnel weakening, and operational hazards.
Solution: The construction team employed polyurethane-based chemical grouting—a method that involves injecting expanding polyurethane resin into the leaking zones. This material reacts with water, expands rapidly, and forms a flexible, impermeable seal.
Outcome:
● Long-term waterproofing was achieved
● Tunnel integrity preserved without structural alteration
● Zero downtime in construction schedule
● The method proved ideal for grouting work in construction under high-moisture and pressure condition.

2.Tehri Dam, Uttarakhand – Foundation Stabilization Using Cement Grouting
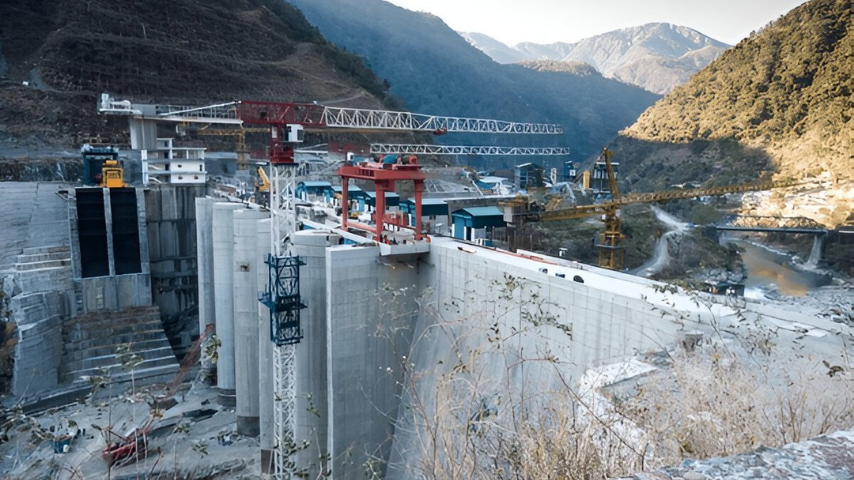

Outcome:
● Rock voids and joints were sealed effectively
● Hydraulic uplift and seepage risks were mitigated
● The grout curtain enhanced structural safety without disturbing the dam body
● A classic use case for cement grouting in construction in India
Location: Tehri Dam Project, Uttarakhand
Problem: The rock foundation beneath this massive hydroelectric dam exhibited seepage paths and permeability, which threatened the long-term safety of the structure. Given the seismic sensitivity of the region, foundation stability was critical.
Solution: Engineers applied high-pressure cement grouting deep into the dam foundation. This involved drilling multiple boreholes and injecting a specially formulated non-shrink cement grout to create a grout curtain—a vertical barrier that reduces water permeability.
3.Soil Settlement in Indian Homes – Residential Foundation Repair
Location: Residential areas in Chennai, Bengaluru, Hyderabad
Problem: Older residential buildings often suffer from foundation cracks and floor settlement due to soil erosion, poor compaction, or water logging—common issues in clay-rich soils of many Indian cities.
Method: Contractors used pressure grouting—a process of injecting cement grout below the sunken slab through strategically drilled holes. The operation was carried out using a portable grouting pump, making it affordable and minimally invasive.
Grouting Equipment in Construction:
● Hand-operated or motorized grouting machine in construction
● Grout mixer and agitator
● Injection packers for controlled delivery
Result:
● Foundation level restored within hours
● Prevented further structural damage
● Improved bearing capacity of underlying soil
● A practical demonstration of grouting in construction in India for residential building.
FAQs on Grouting in Construction
Q1. What is the meaning of grouting in civil engineering?
Grouting is the process of filling voids or cracks in structures or soil with flowable material to strengthen and seal.
Q2. What are the types of grouting in construction?
Cement grouting, chemical grouting, epoxy grouting, bituminous grouting, and soil grouting.
Q3. What machine is used for grouting?
Grouting machines include high-pressure pumps, hand pumps, or specialized jet grouting rigs for deep foundation work.
Q4. Is grout different from mortar?
Yes. Grout is more fluid and used to fill spaces, while mortar is used to bind bricks or blocks.
Q5. Can grouting prevent water leakage?
Absolutely. Especially chemical grouts like polyurethane can seal active leaks in tunnels, dams, and basements.
Grouting Applications by Noah Infrastructures
Noah Infrastructures stands out as the best construction company in Chennai, known for its quality-driven approach, innovative techniques, and on-time project delivery. We use grouting to strengthen foundations, fill structural gaps, and prevent water leakage in our construction projects. From cement grouting for slabs to chemical grouting in basements, our contractors team ensures safe and stable structures for long-term performance.
Conclusion
Grouting in construction is more than just a filler—it’s a critical process that strengthens, seals, supports, and stabilizes various structural elements. From soil stabilization under buildings to anchoring massive machines, grouting continues to be a game-changer in modern civil engineering.
Whether you are a builder, engineer, student, or homeowner—understanding types of grouting in construction, grouting methods, equipment, and materials will help you make informed decisions in any building project.
*** Would you like to keep this guide handy? You can find a Free Grouting in Construction PDF by searching online—it’s available through various educational and engineering resources on Google.

